What Vitamin Is Only Found In Animal Products
We include products in articles we recollect are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small-scale commission.
x Powerful Nutrients Found Only in Meat

Table of Contents
- What Nutrients Are in Meat?
- D3
- B12
- Vitamin A (Retinol)
- Creatine
- Carnitine
- Carnosine
- Heme Iron
- Docosahexaenoic acrid (DHA)
- Eicosapentaenoic Acrid (EPA)
- Taurine
- Other Nutrients in Meat
- Nutrients Only Institute in Meat: The Takeaway
The human body, and its well-nigh free energy-hungry organ, the encephalon, evolved on a diet of mostly meat for nearly two one thousand thousand years . And then information technology's no wonder that meat provides an abundance of essential vitamins and nutrients. Though plants also offer various nutrients, meat provides these nutrients in the forms that our bodies absorb and utilize the best–a concept called bioavailability. Among these bioavailable compounds, there are nutrients but found in meat.
The evolutionary importance of meat explains why vegans and vegetarians are susceptible to numerous nutrient deficiencies and often have to apply supplements.
In this article, we'll explore the top 8 nutrients that can only exist found in appreciable quantities, in meat.
What Nutrients Are in Meat?
Because of an anti-meat trend in mainstream dietary guidelines, meat is often overlooked when people think of nourishing, nutrient-dense foods. Withal the reality is that meat is the nigh food-dense food on earth.
The chart beneath illustrates how a pocket-size pick of animal products offers an array of nutrients.
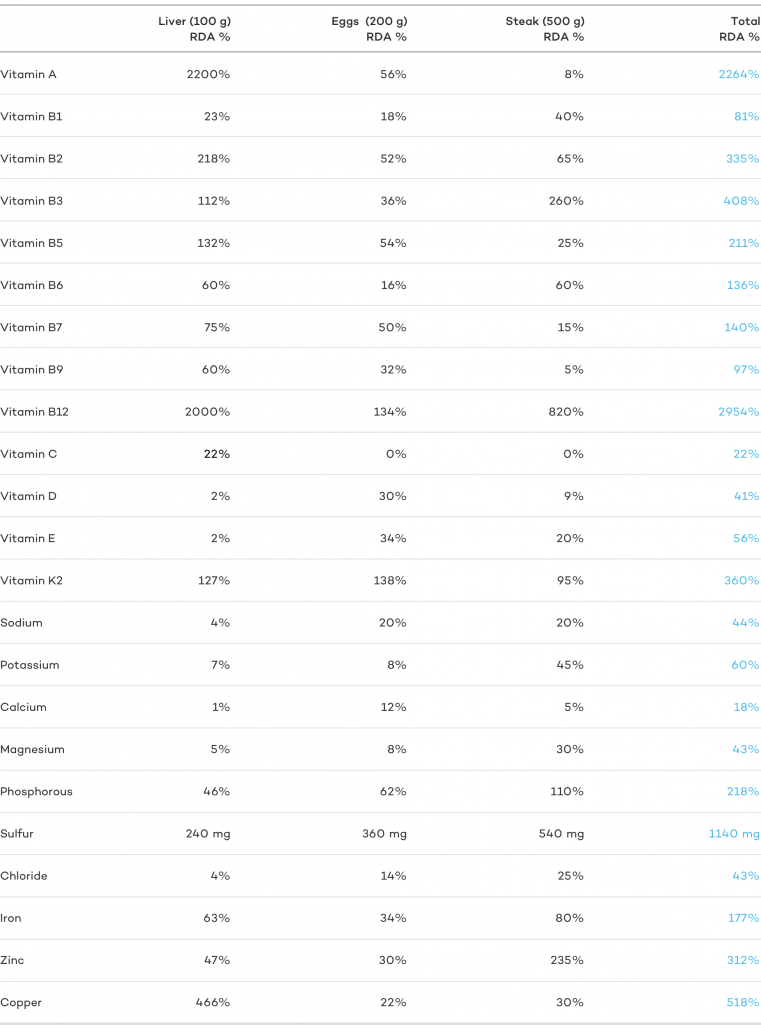
Below are ten of the top nutrients establish only, or in appreciable quantities, in meat:
- D3
- B12
- Vitamin A (Retinol)
- Creatine
- Carnitine
- Carnosine
- Heme iron
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
- Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA)
- Taurine
D3
Vitamin D3 is both a vitamin and a hormone. In add-on to being consumed via foods, your skin can make vitamin D when you get enough sun. This ways vitamin D becomes particularly of import if y'all live in far northern and southern latitudes, and in areas with common cold, cloudy winters.
Dietary vitamin D comes in ii dissimilar forms: at that place'southward ergocalciferol (D2), from plant foods, and cholecalciferol (D3), from animal foods.
Report'due south evidence that cholecalciferol (D3) from brute foods is much more absorbable than its plant-based counterpart. [ ane ] Nature's top D3 sources include fat fish , beef organs , and egg yolks . [ 2 ]
People who don't get enough D3 from diet and sunlight may experience a variety of negative symptoms including depression, multiple sclerosis, and an dumb immune response. Contempo studies testify that vitamin D3 tin assist you fight viral infections including Covid-19 [ 3 ][ 4 ][ 5 ]
B12

Vitamin B12, or cobalamin, is a B vitamin that'due south found primarily in creature foods like meat, fish, cheese, and eggs. [ vi ] This makes B12 hard to obtain for vegans or vegetarians who limit their meat intake. [ 7 ] The symptoms of B12 deficiency include:
- Chronic fatigue [ viii ]
- Psychiatric bug [ 9 ]
- Neurological problems [ x ]
- Increased risks of Alzheimer'south disease [ 11 ]
- Intergenerational neurological disorders [ 12 ]
Meat is a proven source of B12 and other B vitamins. Beef liver is nature's very best source, containing 2,471 percent of your RDA per 100 grams. While chicken liver offers 220% per 100 grams and is more than palatable to most people. You can observe a full beef liver vs. chicken liver comparison here.
While animal products are the all-time source of vitamin B12 by far, a select few found foods likewise contain some quantities:
- Shiitake
- Nori (seaweed) [ 12 ]
- Tempeh (fermented soy) [ thirteen ]
Vitamin A (Retinol)
Vitamin A in the grade of retinol is a fat-soluble vitamin establish exclusively in meat and animal products. It is essential for maintaining vision, concrete developmetn, immune role, and reproduction.
You may have heard that some plants like carrots are high in vitamin A. However, the vitamin A in carrots is in the grade of a caretinoid–a forerunner to vitamin A that the body has to convert into vitamin A. Like the zinc and Fe found in Animal foods, vitamin A retinal is far more bioavailable than it'south institute food counterpart.
Studies have found that retinol absorption efficiency was around 30% in 1 hour, merely less than 5% for vitamin A carotenoids.
If yous don't get vitamin A from your nutrition you will be deficient, resulting in hair loss, skin bug, dry eyes, susceptibility to infections, and blindness at dark.
As a is fat-soluble vitamin, retinal is absorbed into the blood stream and used by the body when consumed alongside brute fat.
Considering that homo physiology evolved on a diet of mostly fatty meat for nearly 2 million years, it's no surprise that most meats that are high in vitamin A are also loftier in fat. This is not the case for institute foods high in caretenoids, which is yet another piece of evidence supporting the view that humans are made to thrive on meat.
The highest retinol foods include:
1. Beef Liver — 713% DV per serving
one slice: six,421 mcg (713% DV) 100 grams: nine,442 mcg (ane,049% DV)
2. Lamb Liver — 236% DV per serving
1 ounce: 2,122 mcg (236% DV) 100 grams: 7,491 mcg (832% DV)
3. Liver Sausage — 166% DV per serving
one slice: 1,495 mcg (166% DV) 100 grams: 8,384 mcg (923% DV)
4. Cod Liver Oil — 150% DV per serving
one teaspoon: 1,350 mcg (150% DV) 100 grams: 30,000 mcg (3,333% DV)
5. King Mackerel — 43% DV per serving
Half a fillet: 388 mcg (43% DV) 100 grams: 252 mcg (28% DV)
Creatine
Creatine is a molecule that provides easy-to-access free energy to your muscles and brain cells.
Creatine may enhance muscle size, strength, and growth, which has made it one of the about pop bodybuilding supplements over the by several decades. [ fourteen ]
Small amounts of creatine can be produced by your liver, but information technology takes much larger amounts of this substance to saturate muscle tissue. [ fifteen ]
Thankfully you tin observe these larger amounts in red meat. Some carnivore diet proponents argue that eating several pounds of meat per day is just as effective as supplementing with creatine. Indeed, studies take shown that creatine supplements may not be of employ to meat-eaters — implying that these groups already have plenty of creatine. [ 16 ]
Eating a vegetarian nutrition, on the other hand, is shown to reduce ane's creatine levels. Vegetarians who partake in creatine-depleting workouts may accept even more trouble maintaining their creatine stores. [ 17 ]
Carnitine
L-carnitine is an amino acid found primarily in fauna foods. While it'southward not technically considered an "essential" amino acid, L-carnitine is nonetheless important. It may turn on 'fat-burning mode' enough to slow the decline of Alzheimer's and increment muscular endurance. [ xviii ]
There isn't yet an established RDA/RDV for L-carnitine, but many groups recommend that dosage in the 2-four grams/day range is well-nigh beneficial. High enough doses may have a cardioprotective consequence. [ nineteen ]
Beef and pork contain the highest amounts of L-carnitine. 3 ounces of beefiness contains ~80 milligrams, three ounces of pork contains ~22 milligrams, and 3 ounces of fish contains ~five milligrams. f
Carnosine
Carnosine is an important antioxidant that'due south establish in the muscles and brain. [ 20 ] Like creatine, carnosine is directly tied to improved muscular strength and endurance. [ 21
While carnosine is considered non-essential, these benefits shouldn't exist ignored.
Meat eaters get their carnosine via two pathways: straight from meat and eggs, and indirectly via beta-alanine (which is likewise found in meat and eggs). Unsurprisingly, vegetarians have lower carnosine levels than carnivores and omnivores do. [ 22 ]
Heme Iron
There are two types of fe: not-heme fe from plants, and heme iron from red meat.
If you've noticed a trend yet, yous can probably deduce that heme fe is better absorbed.
[ 23 ] Meat eaters generally have replete iron levels.
Non-heme iron, on the other hand, is poorly absorbed, and its bioavailability is frequently limited even further by the constitute antinutrients that accompany information technology. These factors make anemia more common in vegans and vegetarians. [ 24 ]
Docosahexaenoic acrid (DHA)
DHA is an omega-iii fatty acid that protects the encephalon from inflammation and oxidative stress. [ 26 ] DHA deficiency tin can crusade severe mental health challenges, specially in children, as they have such quick-growing brains. [ 27 ]
The best sources of DHA include fish, grass-fed beef , pastured eggs , algae, flax seeds, and chia seeds . The healthier an animal was fed and/or raised, the more than omega-3'southward information technology tends to take.
Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA)
EPA is another of import omega-iii fat acid found mostly in cold h2o seafood like salmon, herring, shrimp, eel, and sturgeon.
Some EPA is likewise found in some grass-fed beast foods, including meats and full-fat dairy.
In the trunk, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) tare used to produce signaling molecules called eicosanoids. These molecules play various important roles, including reducing inflammation at the root of numerous modernistic diseases.
Sudies on the effects of fish oil high in both EPA and DHA show reductions in symptoms of low. A report from 2009 found that EPA was showed superior anti-depressive effects compared with DHA.
For menopausal women, EPA has been shown to reduce hot flashes.
Taurine
Taurine is a sulfur-based compound plant throughout the body and its vital organs. The full role of taurine isn't yet known, just it seems to play major roles in antioxidant production, bile table salt production, and muscular part. [ 28 ] Its also factors into :
- Eye health
- Central nervous organization function
- Immune regulation
- Antioxidant effects
- Maintaining hydration and balanced electrolytes
Taurine is only found in animal foods similar beef, fish, and dairy . Dietary taurine likely contributes to your trunk'southward baseline taurine levels. Equally you might expect, that means vegans take lower levels of taurine than omnivores do. [ 29 ]
Other Nutrients in Meat
In addition to the hard-to-find nutrients above, meat is likewise rich in several other vitamins and minerals. Hither are some of the highlights.
Vitamins in meat
- Niacin
- Riboflavin
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin B5
- Vitamin B6
Niacin
Niacin works with other B vitamins to promote intracellular energy production.
In addition to obtaining niacin from diet, your body can synthesize it from dietary tryptophan. The best meats , eggs, cheese , and seafood all contain an affluence of niacin and tryptophan — allowing them to heave your body's levels via both pathways.
Riboflavin
Riboflavin is another pro-metabolic B vitamin. Its top roles include releasing energy from the foods you consume, maintaining skilful vision, and promoting iron uptake.
The best sources of riboflavin are mostly animal foods: meat, milk , cheese , yogurt , are all correct up in that location in terms of riboflavin content.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A is 1 of the most important nutrients for centre and skin health. [ 30 ] Vitamin A may also forestall degenerative heart problems such as:
- Night incomprehension
- Vision loss
- Dry eyes
- Ulcers
Brute foods, and especially beef liver are nature's all-time source of preformed vitamin A. The vitamin A carotenoids in carrots and sweet potatoes are 'precursors' that your trunk must catechumen into usable vitamin A, making them low bioavailability.
Minerals in Meat
- Zinc
- Selenium
- Phosphorus
- Magnesium
- Potassium
Zinc
Red meat is among the very all-time sources of dietary zinc. In improver to having greater amounts of zinc than almost any plant food, the zinc in blood-red meat is 4 times better absorbed. [ 31 ]
Zinc is yet some other nutrient that vegans and vegetarians tend to be running low on — it's hard to hit your zinc RDA solely from plants and grains.
Staying replete in zinc (and copper, which it works closely with) allows your body to carry out several vital functions. In children, zinc promotes motor neuron and cognitive evolution; in adults, it promotes insulin sensitivity and glycemic control. And it's crucial to proper immune part for all ages. [ 32 ]
Selenium
Selenium is a pro-thyroid nutrient that has indirect effects on several physiological functions. It's also especially good for your heart. Most cuts of beef contain 20-thirty micrograms of selenium per three ounces.
Pork is an fifty-fifty ameliorate source of selenium: a cup of roast pork contains 122% of your RDV.
Obtaining your selenium from fauna sources is probable more than of import than ever before since our soils are becoming depleted of it. Selenium is and so of import to immune health that areas with especially low-selenium soil often take college COVID infection rates. [ 33 ]
In the chart of nutrients found in fruits and vegetables beneath y'all can see just how depleted our soils have become over decades of intensive agricultural use. Meat, on the other manus, is not equally susceptible to soil depletion.
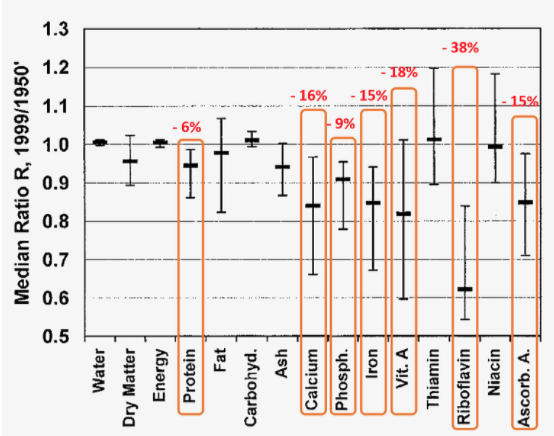
Nutrients Only Found in Meat: The Takeaway
Humans evolved while consuming a carnivorous diet centered on meat. Meat contains a robust combination of vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients, some of which are impossible to get from other food groups, while other non-meat nutrients are poorly captivated by the body.
Red meat, and organ meats in particular, is an exceptional source of:
- D3
- B12
- Taurine
- Creatine
- Carnitine
- Carnosine
- Heme iron
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
No other food group comes shut to providing so many nutrients in their almost bioavailable forms.
Article Sources
Source: https://www.doctorkiltz.com/nutrients-found-only-in-meat/
Posted by: thompsonmorpegir.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Vitamin Is Only Found In Animal Products"
Post a Comment